TWC G6 Livestock Production
New Diseases & Mutation
Health Experts say that more air travel, climate changes and rising demand for meat products are responsible for the spread of zoonotic* diseases like Swine Flu and SARS. From our perspective, all of the above factors including globalisation and increased human interaction livestock can likely result in a global pandemic.
*Zoonotic diseases are defined those which can be passed between vertebrate animals and humans. The term was originally used to describe a group of diseases that humans may acquire from domestic animals. This definition has since been modified to include all human diseases that are acquired from or transmitted to any other vertebrate. Infections may be naturally transmitted between animals and humans.
Zoonotic diseases can be caused by bacteria, viruses, fungi and parasites. Different zoonoses are transmitted to humans in a different ways:
- the disease may be directly infectious,
- it may be transmitted by vectors
- it may be transmitted in food or water.
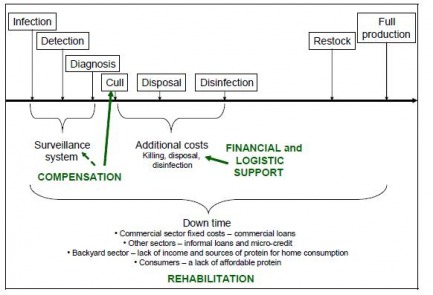
Chain of events due to widespread disease
Source : http://www.fao.org/docs/eims/upload//251044/aj201e00.pdf
Swine influenza (also called swine flu, hog flu, pig flu and sometimes, the swine) is an infection by any one of several types of swine influenza virus. Swine influenza virus (SIV) is any strain of the influenza family of viruses that is endemic in pigs. As of 2009, the known SIV strains include influenza C and the subtypes of influenza A known as H1N1, H1N2, H3N1, H3N2, and H2N3.
Transmission : Swine influenza virus is common throughout pig populations worldwide. Transmission of the virus from pigs to humans is not common and does not always lead to human influenza, often resulting only in the production of antibodies in the blood. If transmission does cause human influenza, it is called zoonotic swine flu. People with regular exposure to pigs are at increased risk of swine flu infection. The meat of an infected animal poses no risk of infection when properly cooked
Sources : http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/H1n1
http://www.who.int/csr/disease/swineflue/en/
Transmission : Swine influenza virus is common throughout pig populations worldwide. Transmission of the virus from pigs to humans is not common and does not always lead to human influenza, often resulting only in the production of antibodies in the blood. If transmission does cause human influenza, it is called zoonotic swine flu. People with regular exposure to pigs are at increased risk of swine flu infection. The meat of an infected animal poses no risk of infection when properly cooked
Sources : http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/H1n1
http://www.who.int/csr/disease/swineflue/en/
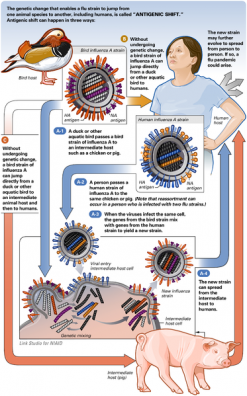
Videos Linking Influenza A to Factory Farming
Transmission : Consumption of infected Cows. Cows get infected when they are given meal and bone meal (MBM), which comprises of 50% protein, 35% ash, 8-12% fat and 4-7% moisture and is said to improve the amino acid profile of the cows.
Sources : http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/BSE
http://www.who.int/zoonoses/diseases/bse/en
Transmission : Salmonella bacteria can survive several weeks in a dry environment and several months in water; thus, they are frequently found in polluted water, contamination from the excrement of carrier animals being particularly important.
Aquatic vertebrates, notably birds and reptiles, are important vectors of salmonella. Poultry, cattle, and sheep being frequently agents of contamination, salmonella can be found in food, particularly meats and raw eggs
Source : http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Salmonella
Aquatic vertebrates, notably birds and reptiles, are important vectors of salmonella. Poultry, cattle, and sheep being frequently agents of contamination, salmonella can be found in food, particularly meats and raw eggs
Source : http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Salmonella
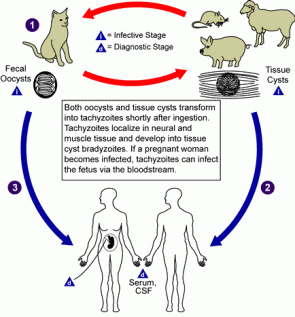
Transmission may occur through:
Source : http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Toxoplasmosis#Transmission
- Ingestion of raw or partly cooked meat, especially pork, lamb, or venison containing Toxoplasma cysts. Infection prevalence in countries where undercooked meat is traditionally eaten has been related to this transmission method. Oocysts may also be ingested during hand-to-mouth contact after handling undercooked meat, or from using knives, utensils, or cutting boards contaminated by raw meat
- Ingestion of contaminated cat faeces. This can occur through hand-to-mouth contact following gardening, cleaning a cat's litter box , contact with children's sandpits, or touching anything that has come into contact with cat faeces.
- Drinking water contaminated with Toxoplasma.
- Transplacental infection in utero.
- Receiving an infected organ transplant or blood transfusion, although this is extremely rare
Source : http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Toxoplasmosis#Transmission
Transmission : Brucellosis in humans is usually associated with the consumption of unpasteurized milk and soft cheeses made from the milk of infected animals, primarily goats, infected with Brucella melitensis and with occupational exposure of laboratory workers, veterinarians and slaughterhouse workers
Source : http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Brucellosis
http://www.smallstock.info/info/zoon/brucellosis.htm
Source : http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Brucellosis
http://www.smallstock.info/info/zoon/brucellosis.htm